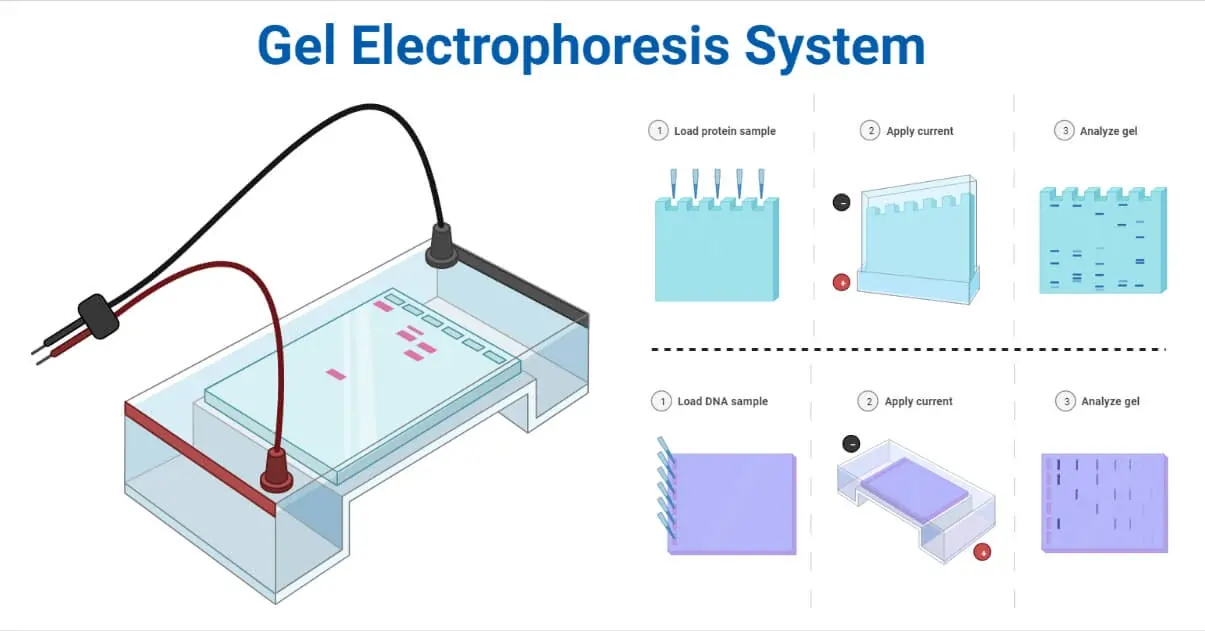
Introduction: Gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool used in molecular biology to separate and analyze DNA, RNA, and proteins. In this post, we will take a closer look at how gel electrophoresis works and how it is used in scientific research.
What is gel
electrophoresis?
Gel electrophoresis is
a technique that uses an electric field to separate molecules based on their
size and charge. It is commonly used to separate and analyze DNA, RNA, and
proteins, and it is an important tool in molecular biology, genetics, and
biochemistry.
How does gel
electrophoresis work?
Gel electrophoresis
involves the use of a special type of gel, called an electrophoresis gel, which
is made from a polymer like agarose or polyacrylamide. The gel is placed in a
special tray, and a sample of the molecules to be analyzed is applied to the gel.
An electric field is then applied, and the molecules begin to move through the
gel.
The molecules will move
at different speeds through the gel based on their size and charge. Smaller
molecules will move more quickly through the gel, while larger molecules will
move more slowly. This allows the molecules to be separated and resolved into
distinct bands on the gel.
After the
electrophoresis is complete, the separated molecules can be visualized using
special dyes or stains. This allows scientists to analyze and compare the
molecules and learn more about their properties and functions.
Uses of gel
electrophoresis:
Gel electrophoresis is
used in a wide variety of scientific applications, including:
DNA sequencing: Gel
electrophoresis is commonly used to separate and analyze DNA fragments, which
can be used to determine the sequence of base pairs in a DNA molecule.
Protein analysis: Gel
electrophoresis can be used to separate and analyze proteins based on their
size and charge, allowing scientists to study the structure and function of
proteins.
Genetic testing: Gel
electrophoresis is often used in genetic testing to identify and characterize
genetic variations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or
mutations.
Forensics: Gel
electrophoresis is sometimes used in forensic science to identify and compare
DNA samples from crime scenes or other sources.
Conclusion: Gel
electrophoresis is an important tool in molecular biology and other scientific
fields, allowing scientists to analyze and compare DNA,
RNA, and proteins. Its
versatility and accuracy make it a valuable tool for a wide range of
applications.
Keywords: gel electrophoresis, molecular biology, DNA, RNA, proteins, electrophoresis gel, agarose, polyacrylamide, DNA sequencing, protein analysis, genetic testing, forensics, capillary electrophoresis.